Last month at the AkronCodeClub they selected the magic square kata, which was a new one for me. Basically, you arrange 9 unique numbers in a 3x3 grid such that they add up to the same number horizontally, vertically and diagonally. I paired up with someone else who knew C#, so it was a good opportunity to try doing the kata in Visual Studio for Mac!
Although I've kicked the tires on VS4Mac a bit, one of the things I hadn't tried testing out was, well.. testing!
Method 1: An NUnit Library Project
In this video I am teaching How can you use your Macbook to develop Csharp or Asp.net core applications using Visual Studio IDE.Copyright© are reserved unde. Node.js Tools for Visual Studio includes support for discovering and executing unit tests. This allows you to author, run, debug, and filter unit tests without having to switch to a command prompt. Use mocha, or simply extend Visual Studio to work with your favorite unit testing framework. CppUTest is a C /C based unit xUnit test framework for unit testing and for test-driving your code. It is written in C but is used in C and C projects and frequently used in embedded systems but it works for any C/C project. CppUTest’s core design principles are: Simple in design and simple in use. Portable to old and new platforms.
The easiest method is to just create a new 'NUnit Library Project'. The VS4Mac team actually added a project type that includes the NUnit package and a test file out of the box. How convenient is that??
Create a new project
Go to: File / New Solution / Other / .NET / NUnit Library Project
Create a class and some tests
Like I said, there's already a 'Test.cs' file ready to go, with the proper NUnit attributes and everything. Go ahead and create a regular class and add a couple tests against it.
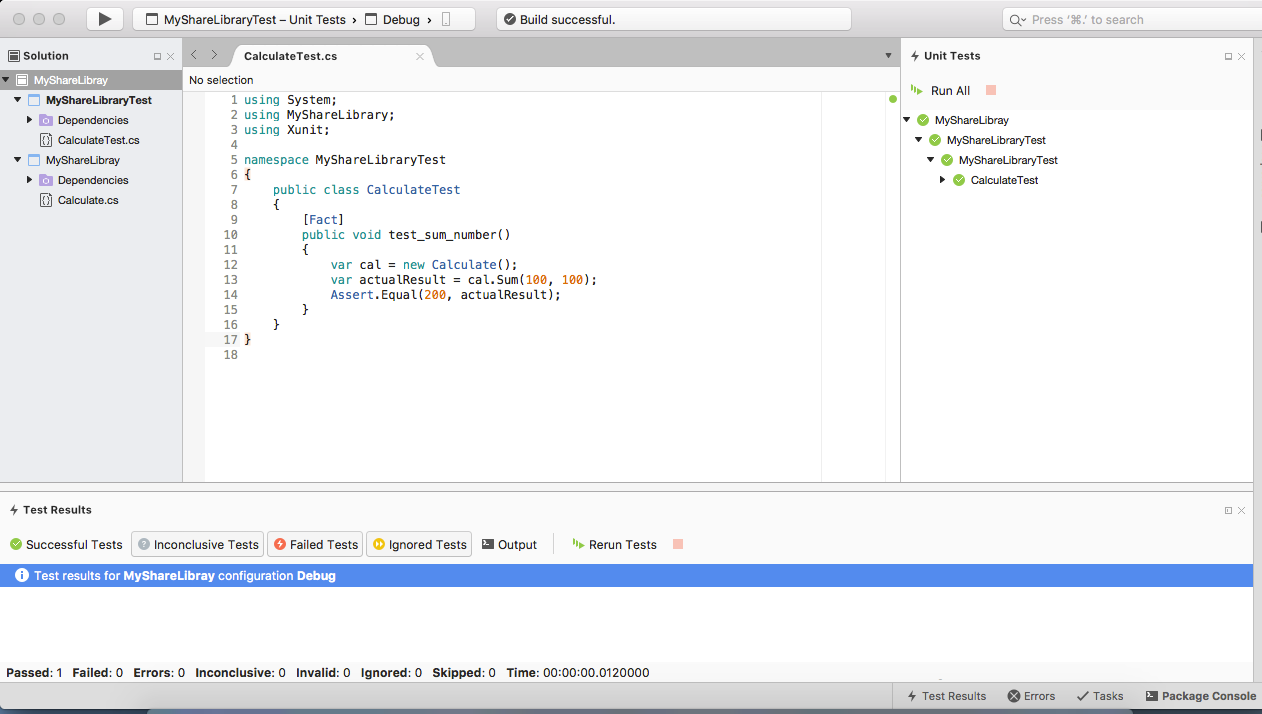
Run the tests
If you can't see the 'Unit Test' pane (or pad as they call it on the Mac), open it now: View / Pads / Unit Tests
You may need to click the build button (black triangle in upper-left) to see your new tests. Or just click the 'Run All' button in the Unit Tests pad.
Now change the logic so the tests fail (if they didn't already) and you can see the failure results in the 'Test Results' pad at the bottom. If you don't see that pad, open it now: View / Pads / Test Results
That's it! If you're using VS4Mac for TDD during a code kata, it doesn't get much easier than that. :)
Method 2: Add NUnit to an Existing Project
But what if you already have a project and now you want to add tests to it? Let's start by creating a Library project to act as the 'existing project': File / New Solution / Other / .NET / Library
You should have a blank screen, along with the 'Solution' pad on the side of the screen. If you don't see that pad, go to: View / Pads / Solution
Create a Test File
Right-click your project and choose Add / New File. Select General / Empty Class and name it 'MagicSquareTests.cs'. I also repurposed the default 'MyClass.cs' as my MagicSquare class. You should end up with something like this:
Add the NUnit Package via NuGet
Right-click on Packages in the Solution pad and choose 'Add Packages'. All you need is NUnit - don't bother with the NUnit Console Runner.
You should see NUnit under the Packages folder.
Create a Few Tests
Add some new tests to run against whatever logic your old project has. In my case, I added a single function for the magic square kata, and wrote a couple tests against it that I was sure would fail.
The test runner tells you what failed and where.
Run / Observe / Fix / Repeat!
Try adding enough code to get your tests to pass, and run again.
More Reading
If you'd like, you can read more about what I've discovered... or just download Visual Studio for Mac and try it out yourself!
-->Use Test Explorer to run unit tests from Visual Studio or third-party unit test projects. You can also use Test Explorer to group tests into categories, filter the test list, and create, save, and run playlists of tests. You can also analyze code coverage and debug unit tests.
Test Explorer can run tests from multiple test projects in a solution and from test classes that are part of the production code projects. Test projects can use different unit test frameworks. When the code under test is written for .NET, the test project can be written in any language that also targets .NET, regardless of the language of the target code. Native C/C++ code projects must be tested by using a C++ unit test framework.
Build your test project
If you do not already have a test project set up in your Visual Studio solution, you must first create and build a test project.
Visual Studio includes the Microsoft unit testing frameworks for both managed and native code. However, Test Explorer can also run any unit test framework that has implemented a Test Explorer adapter. For more information about installing third-party unit test frameworks, see Install third-party unit test frameworks
Run tests in Test Explorer
When you build the test project, the tests appear in Test Explorer. If Test Explorer is not visible, choose Test on the Visual Studio menu, choose Windows, and then choose Test Explorer (or press Ctrl + E, T).
As you run, write, and rerun your tests, Test Explorer displays the results in default groups of Failed Tests, Passed Tests, Skipped Tests and Not Run Tests. You can change the way Test Explorer groups your tests.
As you run, write, and rerun your tests, the Test Explorer displays the results in a default grouping of Project, Namespace, and Class. You can change the way the Test Explorer groups your tests.
You can perform much of the work of finding, organizing and running tests from the Test Explorer toolbar.
Run tests
You can run all the tests in the solution, all the tests in a group, or a set of tests that you select. Do one of the following:
To run all the tests in a solution, choose Run All (or press Ctrl + R, V).
To run all the tests in a default group, choose Run and then choose the group on the menu.
Select the individual tests that you want to run, open the right-click menu for a selected test and then choose Run Selected Tests (or press Ctrl + R, T).
If individual tests have no dependencies that prevent them from being run in any order, turn on parallel test execution with the toggle button on the toolbar. This can noticeably reduce the time taken to run all the tests.
The pass/fail bar at the top of the Test Explorer window is animated as the tests run. At the conclusion of the test run, the pass/fail bar turns green if all tests passed or turns red if any test failed.
You can run all the tests in the solution, all the tests in a group, or a set of tests that you select. Do one of the following:
To run all the tests in a solution, choose the Run All icon (or press Ctrl + R, V).
To run all the tests in a default group, choose the Run icon and then choose the group on the menu.
Select the individual tests that you want to run, open the right-click menu for a selected test and then choose Run Selected Tests (or press Ctrl + R, T).
If individual tests have no dependencies that prevent them from being run in any order, turn on parallel test execution in the settings menu of the toolbar. This can noticeably reduce the time taken to run all the tests.
Run tests after every build
| Button | Description |
|---|---|
| To run your unit tests after each local build, choose Test on the standard menu, and then choose Run Tests After Build on the Test Explorer toolbar. |
Note
Running unit tests after each build requires Visual Studio 2017 Enterprise or Visual Studio 2019. In Visual Studio 2019 it is included in Community and Professional as well as Enterprise.
To run your unit tests after each local build, open the settings icon in the Test Explorer toolbar and select Run Tests After Build.
View test results
As you run, write, and rerun your tests, Test Explorer displays the results in groups of Failed Tests, Passed Tests, Skipped Tests and Not Run Tests. The details pane at the bottom or side of the Test Explorer displays a summary of the test run.
View test details
To view the details of an individual test, select the test.
The test details pane displays the following information:
The source file name and the line number of the test method.
The status of the test.
The elapsed time that the test method took to run.
If the test fails, the details pane also displays:
The message returned by the unit test framework for the test.
The stack trace at the time the test failed.
View the source code of a test method
To display the source code for a test method in the Visual Studio editor, select the test and then choose Open Test on the right-click menu (or press F12).
Group and filter the test list
Test Explorer lets you group your tests into predefined categories. Most unit test frameworks that run in Test Explorer let you define your own categories and category/value pairs to group your tests. You can also filter the list of tests by matching strings against test properties.
Group tests in the test list
To change the way that tests are organized, choose the down arrow next to the Group By button and select a new grouping criteria.
Test Explorer lets you group your tests into a hierarchy. The default hierarchy grouping is Project, Namespace, and then Class. To change the way that tests are organized, choose the Group By button and select a new grouping criteria.
You can define your own levels of the hierarchy and group by State and then Class for example by selecting Group By options in your preferred order.
Test Explorer groups
| Group | Description |
|---|---|
| Duration | Groups test by execution time: Fast, Medium, and Slow. |
| Outcome | Groups tests by execution results: Failed Tests, Skipped Tests, Passed Tests. |
| Traits | Groups test by category/value pairs that you define. The syntax to specify trait categories and values is defined by the unit test framework. |
| Project | Groups test by the name of the projects. |
| Group | Description |
|---|---|
| Duration | Groups tests by execution time: Fast, Medium, and Slow. |
| State | Groups tests by execution results: Failed Tests, Skipped Tests, Passed Tests, Not Run |
| Target Framework | Groups tests by the framework their projects target |
| Namespace | Groups tests by the containing namespace. |
| Project | Groups tests by the containing project. |
| Class | Groups tests by the containing class. |
Traits
A trait is usually a category name/value pair, but it can also be a single category. Traits can be assigned to methods that are identified as a test method by the unit test framework. A unit test framework can define trait categories. You can add values to the trait categories to define your own category name/value pairs. The syntax to specify trait categories and values is defined by the unit test framework.
Traits in the Microsoft Unit Testing Framework for Managed Code
In the Microsoft unit test framework for managed apps, you define a trait name/ value pair in a TestPropertyAttribute attribute. The test framework also contains these predefined traits:
| Trait | Description |
|---|---|
| OwnerAttribute | The Owner category is defined by the unit test framework and requires you to provide a string value of the owner. |
| PriorityAttribute | The Priority category is defined by the unit test framework and requires you to provide an integer value of the priority. |
| TestCategoryAttribute | The TestCategory attribute enables you to specify the category of a unit test. |
| TestPropertyAttribute | The TestProperty attribute enables you to define trait category/value pair. |
Traits in the Microsoft Unit Testing Framework for C++
See How to use the Microsoft Unit Testing Framework for C++.
Create custom playlists

You can create and save a list of tests that you want to run or view as a group. When you select a playlist, the tests in the list are displayed in Test Explorer. You can add a test to more than one playlist, and all tests in your project are available when you choose the default All Tests playlist.
Visual Studio For Mac Unit Test
To create a playlist, choose one or more tests in Test Explorer. On the right-click menu, choose Add to Playlist > NewPlaylist. Save the file with the name and location that you specify in the Create New Playlist dialog box.
To add tests to a playlist, choose one or more tests in Test Explorer. On the right-click menu, choose Add to Playlist, and then choose the playlist that you want to add the tests to.
To open a playlist, choose Test > Playlist from the Visual Studio menu, and either choose from the list of recently used playlists, or choose Open Playlist to specify the name and location of the playlist.
If individual tests have no dependencies that prevent them from being run in any order, turn on parallel test execution with the toggle button on the toolbar. This can noticeably reduce the time taken to run all the tests.
You can create and save a list of tests that you want to run or view as a group. When you select a playlist, the tests in the list are displayed in a new Test Explorer tab. You can add a test to more than one playlist.
To create a playlist, choose one or more tests in Test Explorer. On the right-click menu, choose Add to Playlist > New Playlist.
The playlist opens in a new Test Explorer tab. You can use this playlist once and then discard it, or you can click the Save button in the playlist window's toolbar, and then select a name and location to save the playlist.
To create a playlist, choose one or more tests in Test Explorer. Right-click and choose Add to Playlist > New playlist.
To open a playlist, choose the playlist icon in the Visual Studio toolbar and select a previously saved playlist file from the menu.
To edit a playlist, you can right-click on any test and use the menu options to add or remove it from a playlist.
Starting in Visual Studio 2019 version 16.7, you can choose the Edit button in the toolbar. Check boxes will appear next to your tests showing what tests are included and excluded in the playlist. Edit groups as desired.
You can also check or uncheck the boxes of the parent groups in the hierarchy. This action creates a dynamic playlist that always updates the playlist based on the tests that are in that group. For example, if you place a check mark next to a class, any test added from that class becomes part of this playlist. If you delete a test from that class, it is removed from the playlist. You can learn more about the rules by saving the playlist with the Save button in the toolbar and opening the .playlist file that is created on your disk. This file lists all the rules and individual tests that make up a playlist.
If you would like to make a playlist for traits, use the following format for MSTest.
Use the following format for xUnit. Make sure there is a space between your TestCategory name and the [Value].
Test Explorer columns
The groups are also available as columns in Test Explorer, along with Trait, Stack Trace, Error Message, and Fully Qualified Name. Most columns are not visible by default, and you can customize which columns you see and the order in which they appear.
Filter, sort, and rearrange test columns
Columns can be filtered, sorted, and rearranged.
To filter to specific traits, click the filter icon at the top of the Traits column.
To change the order of the columns, click on a column header and drag it left or right.
To sort a column, click on the column header. Not all columns can be sorted. You can also sort by a secondary column by holding the Shift key and clicking on an additional column header.
Search and filter the test list
You can also use Test Explorer search filters to limit the test methods in your projects that you view and run.
When you type a string in the Test Explorer search box and choose Enter, the test list is filtered to display only those tests whose fully qualified names contain the string.
To filter by a different criteria:
Open the drop-down list to the right of the search box.
Choose a new criteria.
Enter the filter value between the quotation marks. If you want to search for an exact match on the string instead of a containing match use an equals sign (=) instead of the colon (:).
Note
Searches are case insensitive and match the specified string to any part of the criteria value.
| Qualifier | Description |
|---|---|
| Trait | Searches both trait category and value for matches. The syntax to specify trait categories and values are defined by the unit test framework. |
| Project | Searches the test project names for matches. |
| Error Message | Searches the user-defined error messages returned by failed asserts for matches. |
| File Path | Searches the fully qualified file name of test source files for matches. |
| Fully Qualified Name | Searches the fully qualified name of test namespaces, classes, and methods for matches. |
| Output | Searches the user-defined error messages that are written to standard output (stdout) or standard error (stderr). The syntax to specify output messages are defined by the unit test framework. |
| Outcome | Searches the Test Explorer category names for matches: Failed Tests, Skipped Tests, Passed Tests. |
| Qualifier | Description |
|---|---|
| State | Searches the Test Explorer category names for matches: Failed Tests, Skipped Tests, Passed Tests. |
| Traits | Searches both trait category and value for matches. The syntax to specify trait categories and values are defined by the unit test framework. |
| Fully Qualified Name | Searches the fully qualified name of test namespaces, classes, and methods for matches. |
| Project | Searches the test project names for matches. |
| Target Framework | Searches the Test Explorer category names for matches: Failed Tests, Skipped Tests, Passed Tests. |
| Namespace | Searches the test namespaces for matches. |
| Class | Searches the test classes names for matches. |
To exclude a subset of the results of a filter, use the following syntax:
For example, FullName:'MyClass' - FullName:'PerfTest' returns all tests that include 'MyClass' in their name, except tests that also include 'PerfTest' in their name.
Visual Studio For Mac Review
Analyze unit test code coverage
You can determine the amount of product code that is actually being tested by your unit tests by using the Visual Studio code coverage tool that's available in Visual Studio Enterprise edition. You can run code coverage on selected tests or on all tests in a solution.
To run code coverage for test methods in a solution:
Choose Test on the top menu bar and then choose Analyze code coverage.
Choose one of the following commands from the sub-menu:
Selected tests runs the test methods that you have selected in Test Explorer.
All tests runs all the test methods in the solution.
- Right-click in Test Explorer and select Analyze Code Coverage for Selected tests
The Code Coverage Results window displays the percentage of the blocks of product code that were exercised by line, function, class, namespace and module.
For more information, see Use code coverage to determine how much code is being tested.
Test shortcuts
Tests can be run from Test Explorer by right-clicking in the code editor on a test and selecting Run test or by using the default Test Explorer shortcuts in Visual Studio. Some of the shortcuts are context-based. This means that they run or debug tests based on where your cursor is in the code editor. If your cursor is inside a test method, then that test method runs. If your cursor is at the class level, then all the tests in that class run. This is the same for the namespace level as well.
| Frequent Commands | Keyboard Shortcuts |
|---|---|
| TestExplorer.DebugAllTestsInContext | Ctrl+R, Ctrl+T |
| TestExplorer.RunAllTestsInContext | Ctrl+R, T |
| TestExplorer.RunAllTests | Ctrl+R, A |
| TestExplorer.RepeatLastRun | Ctrl+R, L |
Visual Studio For Mac Unit Test Free
Note
You can't run a test in an abstract class, because tests are only defined in abstract classes and not instantiated. To run tests in abstract classes, create a class that derives from the abstract class.
Test audio cue
Visual Studio For Mac Download
Test Explorer can play a sound when a test run completes. There are two sounds: one sound to indicate the test run succeeded with all passing tests, and a second sound to indicate the test run completed with at least one failing test. You can set up these sounds in the default Windows 10 sound dialog. This feature is available starting in Visual Studio 2019 Update 16.9 Preview 3.
Visual Studio For Mac Debug Unit Test
- Open the default Windows 10 sound dialog.
- Navigate to the Sounds tab.
- Find the Microsoft Visual Studio category. Choose the Test Run Succeeded or Test Run Failed sounds to select the preset sounds or browse to your own audio file.